From Hatcheries to Habitat? Look Again. Trout Magazine
This commodity is an excerpt from Diminutive Habits, my New York Times bestselling volume.
Your life today is essentially the sum of your habits.
How in shape or out of shape yous are? A upshot of your habits.
How happy or unhappy you are? A consequence of your habits.
How successful or unsuccessful you lot are? A result of your habits.
What yous repeatedly do (i.due east. what you spend fourth dimension thinking about and doing each solar day) ultimately forms the person you are, the things you lot believe, and the personality that you portray.
But what if y'all desire to ameliorate? What if yous desire to class new habits? How would you get about it?
Turns out, there's a helpful framework that can go far easier to stick to new habits so that you can meliorate your health, your work, and your life in general.
Permit's talk most that framework now…
The Science of How Habits Work
The procedure of building a addiction can be divided into four uncomplicated steps: cue, peckish, response, and reward.1Breaking it downward into these key parts can help united states sympathize what a habit is, how information technology works, and how to better information technology.
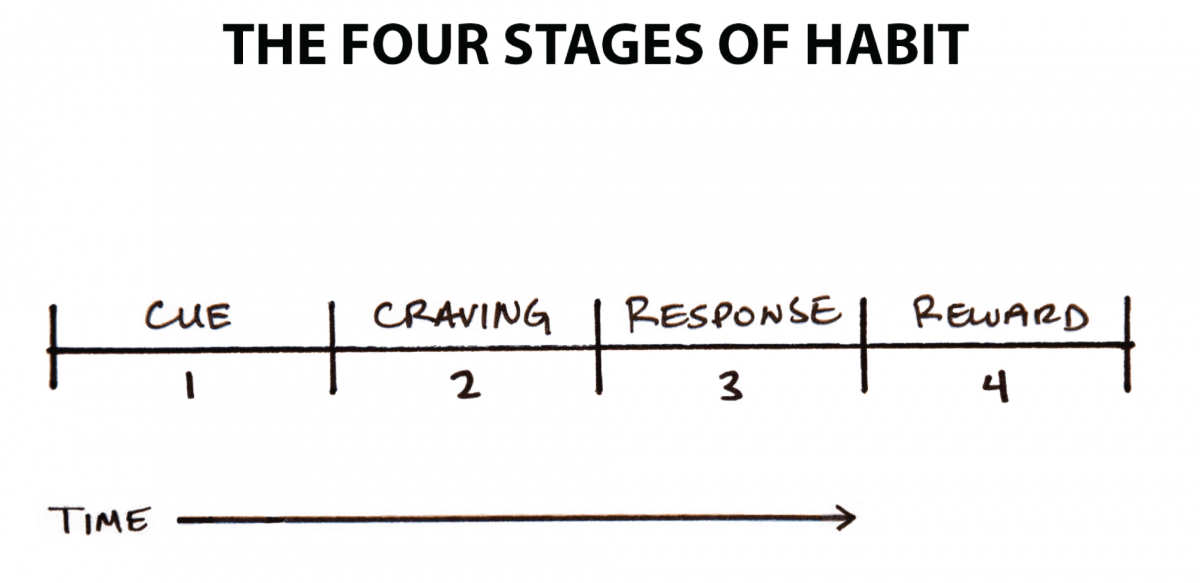
This 4-step pattern is the backbone of every habit, and your brain runs through these steps in the aforementioned order each time.
First, in that location is the cue. The cue triggers your encephalon to initiate a beliefs. It is a bit of information that predicts a reward. Our prehistoric ancestors were paying attention to cues that signaled the location of primary rewards like food, water, and sexual practice. Today, we spend nigh of our fourth dimension learning cues that predict secondary rewards like coin and fame, power and condition, praise and blessing, love and friendship, or a sense of personal satisfaction. (Of grade, these pursuits also indirectly improve our odds of survival and reproduction, which is the deeper motive backside everything we exercise.)
Your mind is continuously analyzing your internal and external environment for hints of where rewards are located. Because the cue is the first indication that we're close to a reward, it naturally leads to a craving.
Cravings are the 2d step of the habit loop, and they are the motivational force backside every addiction. Without some level of motivation or desire—without peckish a change—we take no reason to act. What yous crave is not the habit itself simply the change in country it delivers. You practise not require smoking a cigarette, y'all crave the feeling of relief it provides. You are non motivated past brushing your teeth but rather by the feeling of a clean mouth. Yous do not want to turn on the television, you want to be entertained. Every craving is linked to a want to alter your internal state. This is an important signal that nosotros volition talk over in particular later.
Cravings differ from person to person. In theory, whatever piece of information could trigger a craving, merely in practice, people are not motivated by the aforementioned cues. For a gambler, the sound of slot machines can be a potent trigger that sparks an intense wave of desire. For someone who rarely gambles, the jingles and chimes of the casino are just background racket. Cues are meaningless until they are interpreted. The thoughts, feelings, and emotions of the observer are what transform a cue into a craving.
The third step is the response. The response is the actual addiction y'all perform, which can take the course of a thought or an action. Whether a response occurs depends on how motivated you are and how much friction is associated with the behavior. If a particular action requires more concrete or mental effort than you are willing to expend, and so you won't exercise it. Your response also depends on your power. It sounds simple, but a habit tin occur just if you are capable of doing it. If you want to dunk a basketball only can't jump high enough to reach the hoop, well, you're out of luck.
Finally, the response delivers a reward. Rewards are the finish goal of every habit. The cue is about noticing the reward. The craving is about wanting the reward. The response is about obtaining the reward. Nosotros chase rewards because they serve two purposes: (1) they satisfy us and (2) they teach u.s.a..
The first purpose of rewards is to satisfy your peckish. Yes, rewards provide benefits on their own. Nutrient and water deliver the energy y'all need to survive. Getting a promotion brings more than money and respect. Getting in shape improves your wellness and your dating prospects. Simply the more immediate benefit is that rewards satisfy your craving to eat or to proceeds status or to win blessing. At to the lowest degree for a moment, rewards evangelize contentment and relief from craving.
2nd, rewards teach united states which deportment are worth remembering in the future. Your brain is a reward detector. Every bit yous go about your life, your sensory nervous organisation is continuously monitoring which deportment satisfy your desires and deliver pleasure. Feelings of pleasure and disappointment are role of the feedback mechanism that helps your encephalon distinguish useful actions from useless ones.2 Rewards close the feedback loop and consummate the habit bike.
If a behavior is insufficient in any of the 4 stages, information technology volition not get a habit. Eliminate the cue and your habit will never start. Reduce the craving and you lot won't experience plenty motivation to human action. Make the beliefs difficult and you won't be able to do it. And if the reward fails to satisfy your desire, then you'll have no reason to do it again in the future. Without the first three steps, a behavior will not occur. Without all four, a beliefs volition not be repeated.
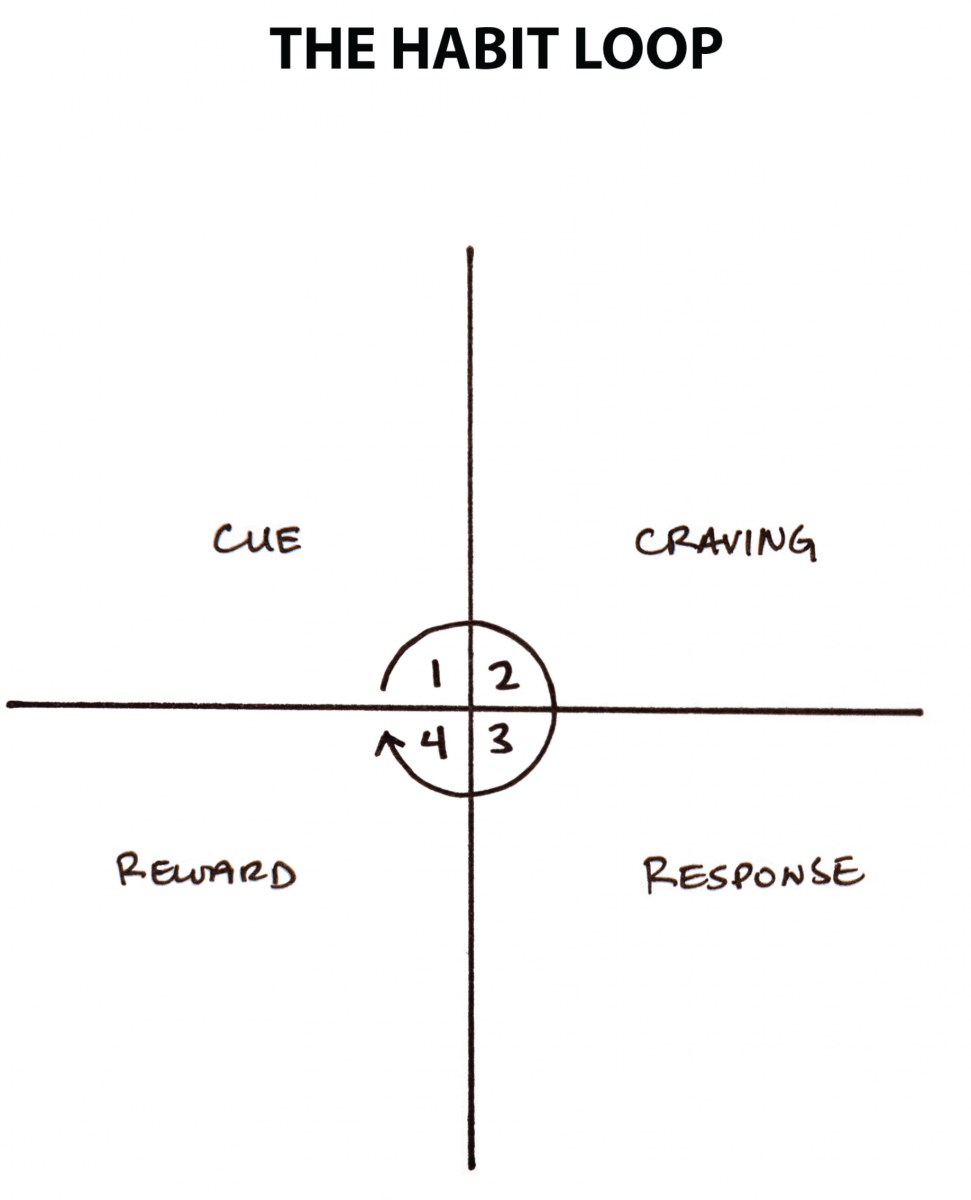
In summary, the cue triggers a peckish, which motivates a response, which provides a reward, which satisfies the craving and, ultimately, becomes associated with the cue. Together, these four steps course a neurological feedback loop—cue, craving, response, reward; cue, peckish, response, advantage—that ultimately allows you lot to create automatic habits.
Nosotros can split these four steps into two phases: the problem stage and the solution phase. The problem phase includes the cue and the peckish, and information technology is when you realize that something needs to alter. The solution phase includes the response and the reward, and information technology is when you take action and accomplish the change y'all desire.
All behavior is driven by the desire to solve a trouble. Sometimes the trouble is that you notice something good and yous desire to obtain it. Sometimes the trouble is that you are experiencing pain and yous want to salvage it. Either manner, the purpose of every habit is to solve the issues you confront.
Permit'southward comprehend a few examples of what this looks like in real life.
| Problem stage | Solution phase | ||
| 1. Cue | 2. Peckish | 3. Response | 4. Reward |
| Your phone buzzes with a new text message. | Yous desire to learn the contents of the message. | You grab your phone and read the text. | You satisfy your craving to read the bulletin. Grabbing your phone becomes associated with your phone buzzing. |
| You are answering emails. | You lot begin to feel stressed and overwhelmed by work. You desire to feel in control. | Y'all bite your nails. | Yous satisfy your craving to reduce stress. Biting your nails becomes associated with answering email. |
| Yous wake up. | You want to feel alert. | You drink a cup of coffee. | You satisfy your craving to experience alert. Drinking coffee becomes associated with waking up. |
| You smell a doughnut shop equally you walk down the street well-nigh your office. | You begin to crave a doughnut. | You purchase a doughnut and eat it. | You satisfy your craving to eat a doughnut. Buying a doughnut becomes associated with walking downward the street near your office. |
| You hit a stumbling block on a project at work. | You lot feel stuck and desire to relieve your frustration. | You pull out your phone and check social media. | You satisfy your peckish to experience relieved. Checking social media becomes associated with feeling stalled at work. |
This four-step process is not something that happens occasionally, only rather it is an endless feedback loop that is running and active during every moment you are alive—even now. The encephalon is continually scanning the environment, predicting what volition happen next, trying out different responses, and learning from the results. The entire process is completed in a split 2nd, and we use information technology again and again without realizing everything that has been packed into the previous moment.
Imagine walking into a night room and flipping on the light switch. You have performed this simple addiction so many times that information technology occurs without thinking. You proceed through all four stages in the fraction of a 2nd. The urge to act strikes you without thinking.
| Problem phase | Solution phase | ||
| 1. Cue | 2. Craving | 3. Response | 4. Reward |
| You walk into a night room. | You want to exist able to come across. | You lot flip the light switch. | You satisfy your craving to encounter. Turning on the low-cal switch becomes associated with being in a dark room. |
By the fourth dimension we become adults, we rarely notice the habits that are running our lives. Most of us never requite a 2d thought to the fact that we tie the aforementioned shoe first each morning, or unplug the toaster later each use, or always modify into comfortable dress afterward getting domicile from work. Afterward decades of mental programming, nosotros automatically skid into these patterns of thinking and acting.
Where to Go From Here
Nosotros can transform these four steps into a practical framework that nosotros can utilize to pattern good habits and eliminate bad ones.
I refer to this framework as the Four Laws of Behavior Change, and it provides a uncomplicated set of rules for creating good habits and breaking bad ones. You can think of each law as a lever that influences human beliefs. When the levers are in the right positions, creating good habits is effortless. When they are in the wrong positions, it is most impossible.
| How to Create a Proficient Habit | |
| The 1st law (Cue) | Make it obvious. |
| The 2nd law (Peckish) | Make it attractive. |
| The 3rd law (Response) | Brand it piece of cake. |
| The 4th law (Advantage) | Make information technology satisfying. |
We can invert these laws to learn how to break a bad habit.
| How to Break a Bad Habit | |
| Inversion of the anest police force (Cue) | Make information technology invisible. |
| Inversion of the 2nd police force (Craving) | Go far unattractive. |
| Inversion of the 3rd law (Response) | Make it difficult. |
| Inversion of the 4th law (Reward) | Make it unsatisfying. |
Whenever you want to alter your behavior, yous can only enquire yourself:
- How tin can I make it obvious?
- How tin can I make it attractive?
- How can I make it easy?
- How can I get in satisfying?
Information technology would be irresponsible for me to claim that these four laws are an exhaustive framework for changing whatever human behavior, merely I think they're close.
If you have ever wondered, "Why don't I do what I say I'k going to do? Why don't I lose the weight or stop smoking or relieve for retirement or start that side concern? Why do I say something is important but never seem to make time for information technology?" The answers to those questions can be constitute somewhere in these iv laws. The key to creating good habits and breaking bad ones is to sympathize these fundamental laws and how to alter them to your specifications. Every goal is doomed to fail if it goes against the grain of human nature.
This article is an excerpt from Chapter 3 of my New York Times bestselling book Atomic Habits. Read more than here.
Source: https://jamesclear.com/three-steps-habit-change
0 Response to "From Hatcheries to Habitat? Look Again. Trout Magazine"
Post a Comment